For ages, the vast universe has fascinated the human mind. The night sky on which the twinkling stars seem to be embedded, the dark and the boundless space, the unimaginable edge of the universe, or the unsettling thought of being alone in space. These intriguing truths have captivated humanity, driving tireless efforts to solve these riddles.
Space is immense. It is difficult to grasp the tremendous distances between things in our solar system and beyond. In the Workshop “Wandering through the Solar System” At Space, students calculate the relative sizes of the planets and the distances between planets in our solar system. They will then build a model displaying those distances to relative scale and compare it to a conventional solar system diagram. It is a complete STEM workshop in which students take on the engineering task of making a walk-through model of a solar system employing mathematical abilities and various equipment while using scientific concepts to create a scaled-down solar system.
Whether it be the Babylonians who first recorded the appearance of the Hailey’s comet or the Greek astronomers whose contributions to astronomy are significant or the Indian astronomers who were able to conclude that the Earth rotates on its own axis, shows that the ancient civilizations were equally active as contemporary humans to explore the unknown and infinite space.

Source: https://edgeofspace.in/ancient-astronomy-a-brief-history/
The term cosmology describes the study of the universe, its origin, nature, and structure. One of the fascinating questions that still puzzles scientists is how the universe or the cosmos came into existence! However, various theories have been formulated to decipher the origin of the universe viz. the steady state, the big bang, or the pulsating theory. Among these hypotheses, the widely accepted one is the Big Bang theory proposed by the Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître in 1927.

Source: https://open.maricopa.edu/physicalgeology/chapter/22-1-starting-with-a-bigbang/NASA
According to the Big Bang theory, roughly 13.8 billion years ago, there was nothing, but the entirety of the universe existed as a singular, infinitely compressed point known as singularity. It is a single point of infinite density and temperature, which exploded and expanded faster than the speed of light and is still expanding. With the expansion, the universe was cooling down.
In the fraction of seconds after the Big Bang explosion, the fundamental particles such as quarks formed followed by the creation of electrons, photons, and neutrinos. Within just one second, quarks combined together, initiating the formation of neutrons and protons. Three seconds later, neutrons & protons fused together to produce the first-ever nuclei of hydrogen, helium, and traces of lithium. This process by which nuclei are formed is referred to as nucleosynthesis.
Approximately 370,000 years following the Big Bang, the universe had cooled sufficiently for electrons to combine with lighter nuclei, which resulted in the formation of neutral hydrogen atoms. The universe during that period was filled with the mist of these atoms which constituted the primordial gas. Cosmologists refer to this era as “the dark age,” which persisted until the birth of the first-ever star.
As the gas clouds came closer under the influence of gravity, a protostar was produced which further accumulated gases from the surrounding. This escalated the gravitational force, and the core became denser and hotter, leading to the onset of a nuclear fusion reaction inside the core.
This process marked the birth of the first stars in which the gravitational force was in equilibrium with the outward pressure generated by the nuclear fusion in the core. The early stars were hotter and more luminous than our Sun.
Eventually, the formation of stars and the gases around, led to the evolution of galaxies. Elements up to iron were produced inside the stellar core while, at the end of their lives they underwent supernova explosions emitting heavier elements into the interstellar medium. These elements contributed to the chemical diversity of subsequent stellar generations. It has shaped the formation of planets and influenced the composition of galaxies and the present-day universe in which we reside.
The Big Bang occurred at midnight on January 1st in this representation, and the current time corresponds to the last moments of December 31 right before midnight where humans came into existence. There are 1.575 million years per cosmic hour, 37.8 million years per cosmic day, and 437.5 years per cosmic second at this size.
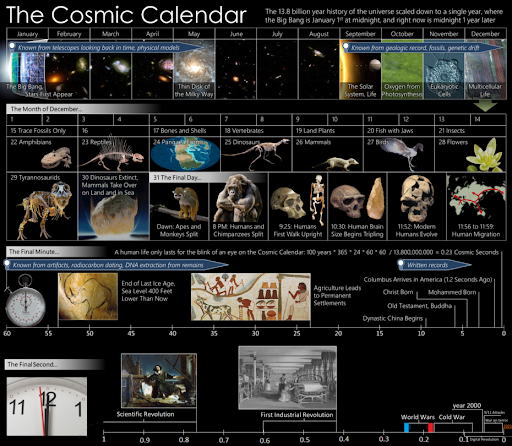
The Cosmic Calendar is a technique for visualizing the universe’s chronology. It reduces the universe’s currently estimated age of 13.8 billion years to a single year to make it easier to understand for educational purposes in popular science or science education.
The sky has always been a fascination. Whenever we look towards it, we all wonder what is up there. How did we come into existence? How big is the universe? Is there anyone else out there like us? Multiverse: real or just a theory? Countless other questions are yet to be answered. Exploring all these unraveled things includes observation, experimentation, and many other skills. The Astronomy Camp at Space India is one such program to instill the scientific temperament in participants to be the discoverers of the universe’s mysteries. Once encouraged, this inquisitiveness never ends and leads to new beginnings.
From its humble beginnings to the vast expanse, we gaze upon today, the cosmos is a testament to humanity’s boundless curiosity and ingenuity.
—
If you like the blog, enroll your school or yourself (k-12 student) in our School Programs or Online Programs, call us at +91-74020 74020 or write to us for any query: getintouch@space-india.com

