Introduction
The Starlink program, developed by SpaceX, is revolutionizing global connectivity by using satellite constellations to provide internet access across the globe. With thousands of satellites already in orbit, Starlink is expanding internet coverage to remote and underserved areas, filling critical gaps in global communication infrastructure.
A recent milestone came on Tuesday, September 24 at 9:01 p.m. PT (Pacific Time), when SpaceX’s Falcon 9 launched 20 new Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. This launch brings enhanced capabilities, including 13 Direct to Cell satellites to improve cellular service in hard-to-reach areas.

At Space India, Through Space Explorers Workshop, Space Satellite, Students learn about various types of satellites that have many different uses that include communication, weather forecasting, navigation, and a lot more. They investigate what is a satellite and learn about the basic parts of the satellite by assembling these parts to make a model of a satellite. Satellites have revolutionized the way we look at the world. These satellites continue to develop our understanding of our own Earth and the universe in the best way possible.
Why Was Starlink Launched?
The Starlink program was launched to solve the global digital divide by delivering high-speed, low-latency internet to underserved and remote areas where traditional infrastructure, like fibre-optic cables and cell towers, is too costly or impractical to build. Over 3 billion people still lack reliable internet access, particularly in rural areas, developing countries, and disaster-prone regions.
Starlink’s goal is not only to provide global internet access but also to generate revenue that will help fund SpaceX’s other ambitious projects, including the development of the Starship spacecraft for missions to Mars and beyond. Moreover, Elon Musk envisions Starlink playing a key role in supporting future interplanetary communication.
A Game-Changing Launch: Starlink Expands
The September 24 launch marked a significant milestone for Starlink. In addition to the 20 new satellites deployed, Direct to Cell technology was introduced, enabling satellites to provide cellular service in regions with little to no coverage. This means that Starlink satellites can now support mobile connectivity even in the most isolated places.
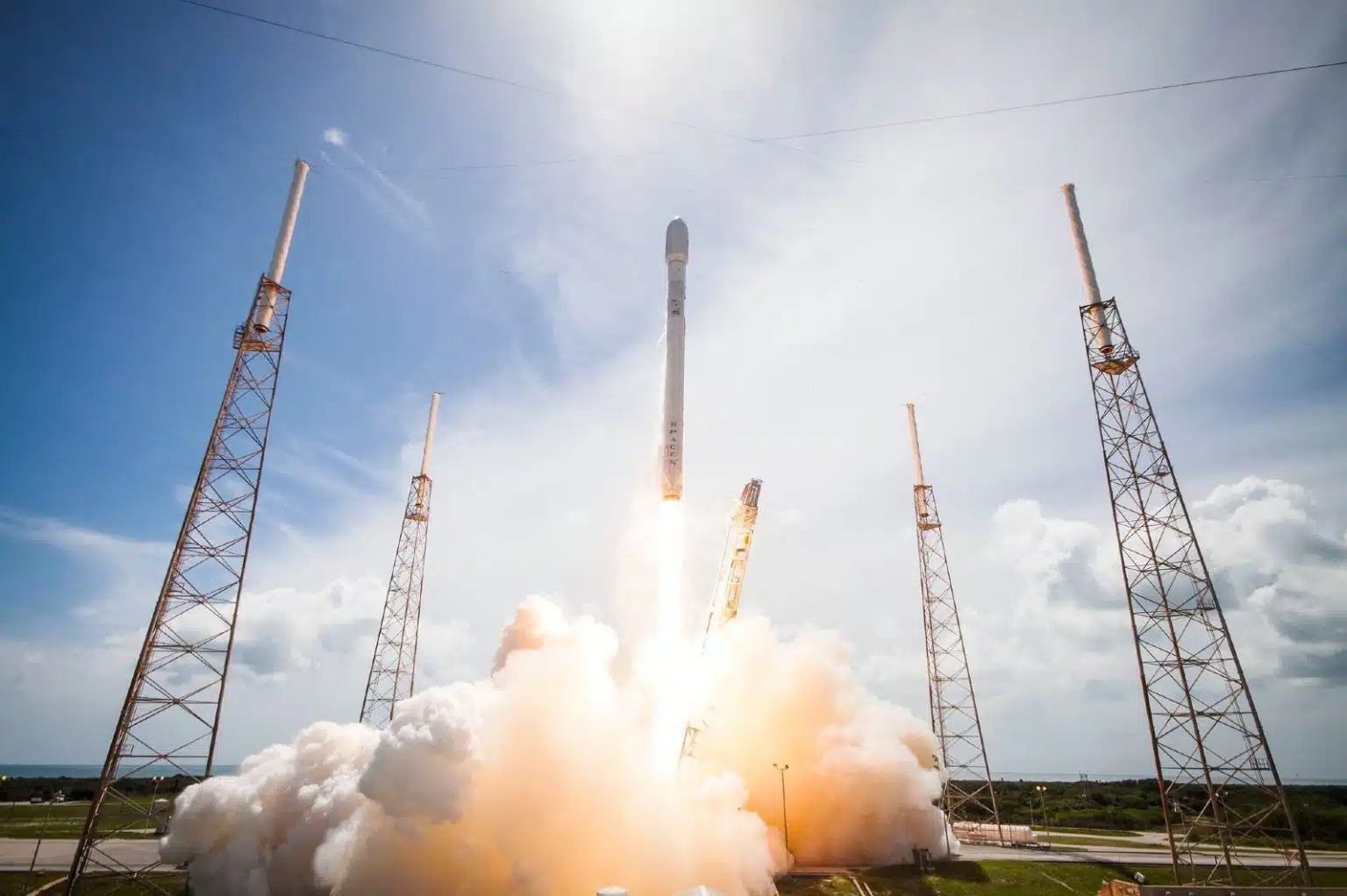

This was also the 10th flight for the Falcon 9 first-stage booster, showcasing SpaceX’s dedication to reusable rocket technology. This booster had previously supported high-profile missions, including NASA Crew-7 and four prior Starlink missions. Reusability is a cornerstone of SpaceX’s strategy, allowing for more cost-effective and frequent launches.
Direct to Cell: Enhancing Connectivity
The introduction of direct-to-cell satellites is a breakthrough in global cellular coverage. This technology will allow mobile phones to connect directly to Starlink satellites, bypassing the need for traditional cell towers
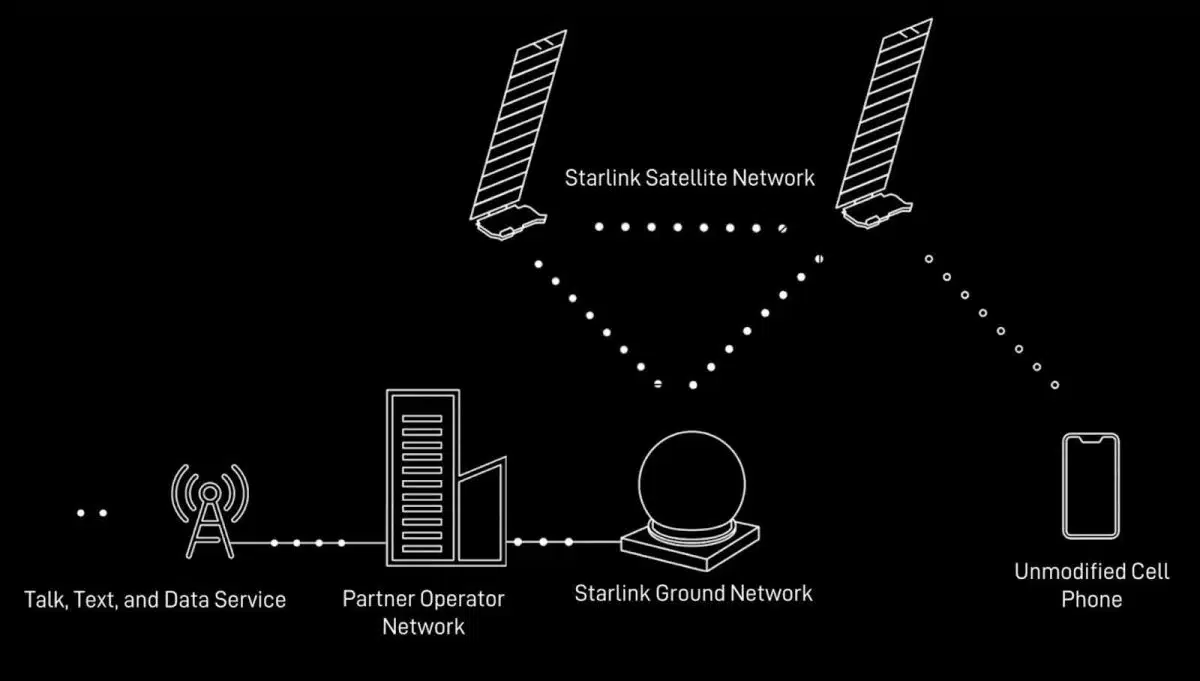
Why is this important?
- Coverage in Remote Areas: Many regions still lack reliable cellular service. With Direct to Cell, users in deserts, mountains, and oceans can now stay connected.
- Seamless Communication: This development could eliminate dropped calls and dead zones, ensuring continuous connectivity regardless of location.
Starlink’s Broader Impact on Global Connectivity
Starlink aims to bridge the digital divide by providing fast, reliable internet where traditional ISPs (Internet Service Providers) fail. With speeds reaching up to 250 Mbps and low-latency performance, Starlink has already improved communication in rural communities and disaster zones, offering quick deployment during emergencies.
Key Benefits:
- Rural and Underserved Areas: Starlink is a game-changer for communities that lack internet access, allowing businesses, healthcare, and education to thrive in previously disconnected regions.
- Disaster Relief: In times of crisis, Starlink has proven to be a lifeline, restoring communication quickly in areas where terrestrial infrastructure has been damaged.
Challenges and the Future of Starlink
Though Starlink is transformative, it faces some challenges:
- Cost: The hardware setup costs about $599, with a monthly subscription of $110, which may be prohibitive for some users, especially in developing regions.
- Space Debris: With thousands of satellites in orbit and more planned, concerns about space debris and congestion are growing.
- Impact on Astronomy: Bright satellite reflections have impacted astronomical observations, though SpaceX is working to mitigate this.
Looking ahead, SpaceX plans to integrate Direct to Cell with mobile networks, improving global coverage even further. As more satellites are launched and new technology is deployed, Starlink will continue to reshape the global communications landscape.
Conclusion
The September 24 launch is a significant step forward for Starlink, which continues to build a more connected world. With advancements like Direct to Cell and a rapidly growing satellite network, SpaceX is redefining how we think about internet access and global communication.
Starlink’s mission to bridge the digital divide, combined with its role in future space exploration, positions it as a key player in the world’s technological evolution.
—
If you like the blog, enrol your school or yourself (k-12 student) in our School Programs or Online Programs, call us at +91-74020 74020 or write to us for any query: getintouch@space-india.com

